Mesopotamian mythology
Mesopotamian mythology
bronze-age

Mesopotamian Religion
Mesopotamian religion refers to the religious beliefs and practices of the civilizations of ancient Mesopotamia, particularly Sumer, Akkad, Assyria and Babylonia between circa 3500 BC and 400 AD, after which they largely gave way to Syriac Christianity.
Some of the most famous myths of Mesopotamian mythology include the creation myth Enuma Elish, the epic of Gilgamesh, and the story of Inanna's descent to the underworld. Enuma Elish describes the creation of the world and the gods by the god Marduk, while the epic of Gilgamesh tells the story of a king's quest for immortality. The story of Inanna's descent to the underworld tells of the goddess's journey to the land of the dead and her eventual return to the world of the living. Other notable myths include the story of the god Enki and the goddess Ninhursag, the myth of Ishtar's descent to the underworld, and the story of the god Dumuzid and his sister Geshtinanna.
The Epic of Gilgamesh
The Epic of Gilgamesh is one of the most famous and important works of ancient Mesopotamian literature. It is an epic poem that tells the story of Gilgamesh, the king of Uruk, and his quest for immortality. The poem is thought to have been written around 2100 BCE, in the Sumerian language, but it was later translated into Akkadian.
The epic tells the story of Gilgamesh's adventures, including his friendship with the wild man Enkidu and their journey to the Cedar Forest to fight the monster Humbaba. After Enkidu's death, Gilgamesh becomes obsessed with the fear of his own mortality and sets out on a journey to find the secret of immortality. He eventually meets Utnapishtim, the only human who has been granted immortality by the gods, and learns the secret of eternal life but fails to achieve it.
The epic also explores themes of friendship, loss, and the human condition, and it is considered one of the earliest known works of literature in world history. The poem was widely read in ancient Mesopotamia and had a significant influence on later literature in the region. The epic of Gilgamesh is still widely read and studied today, both for its historical and literary significance.
Mesopotamian mythology Legends
Ninurta
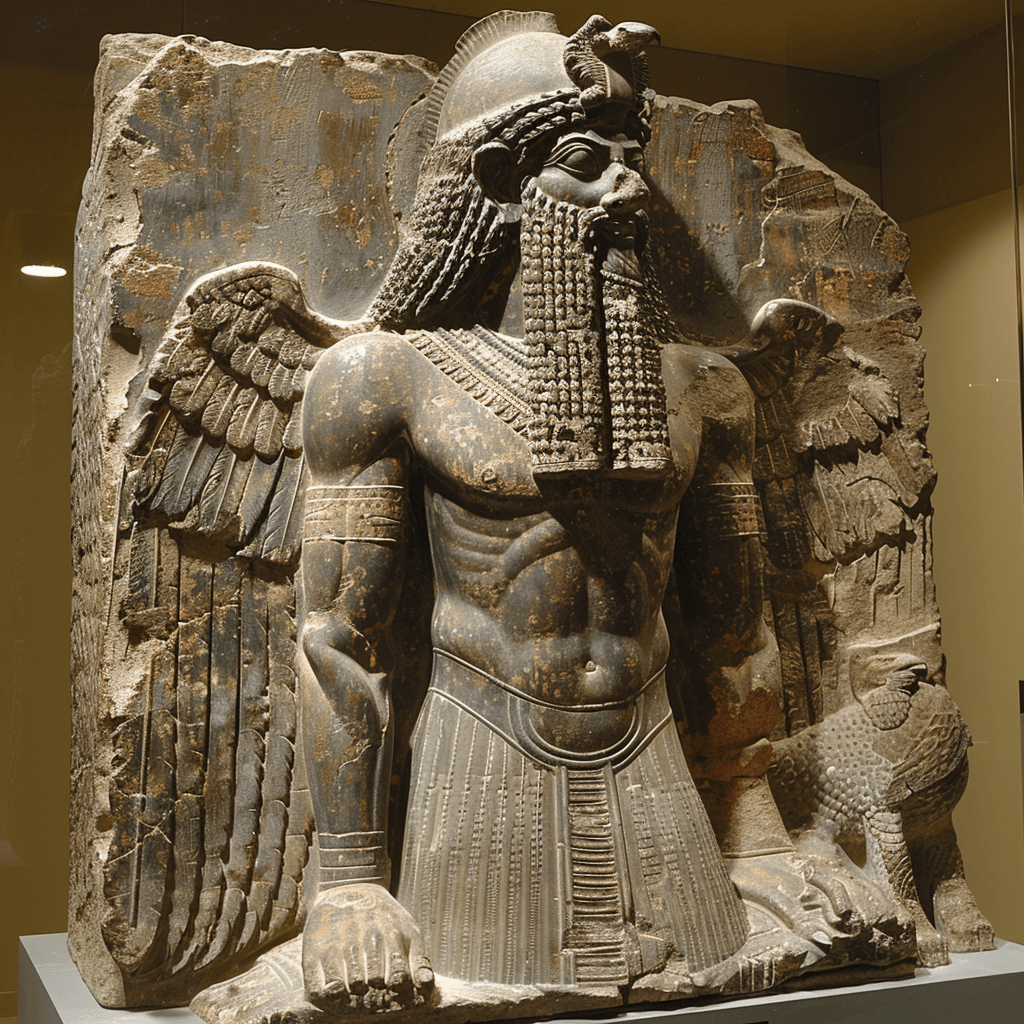

Utu (Shamash)
Marduk
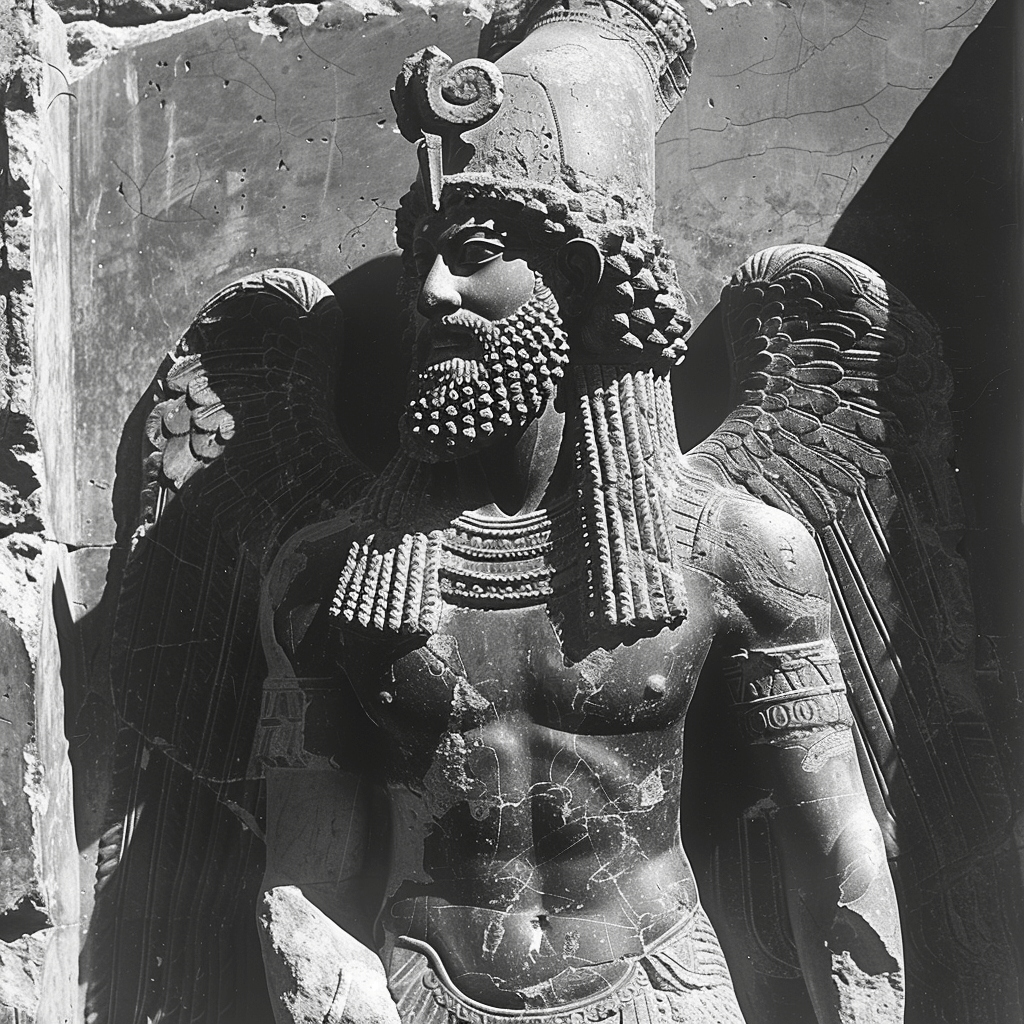

Anu
Ea (Enki)
Gilgamesh
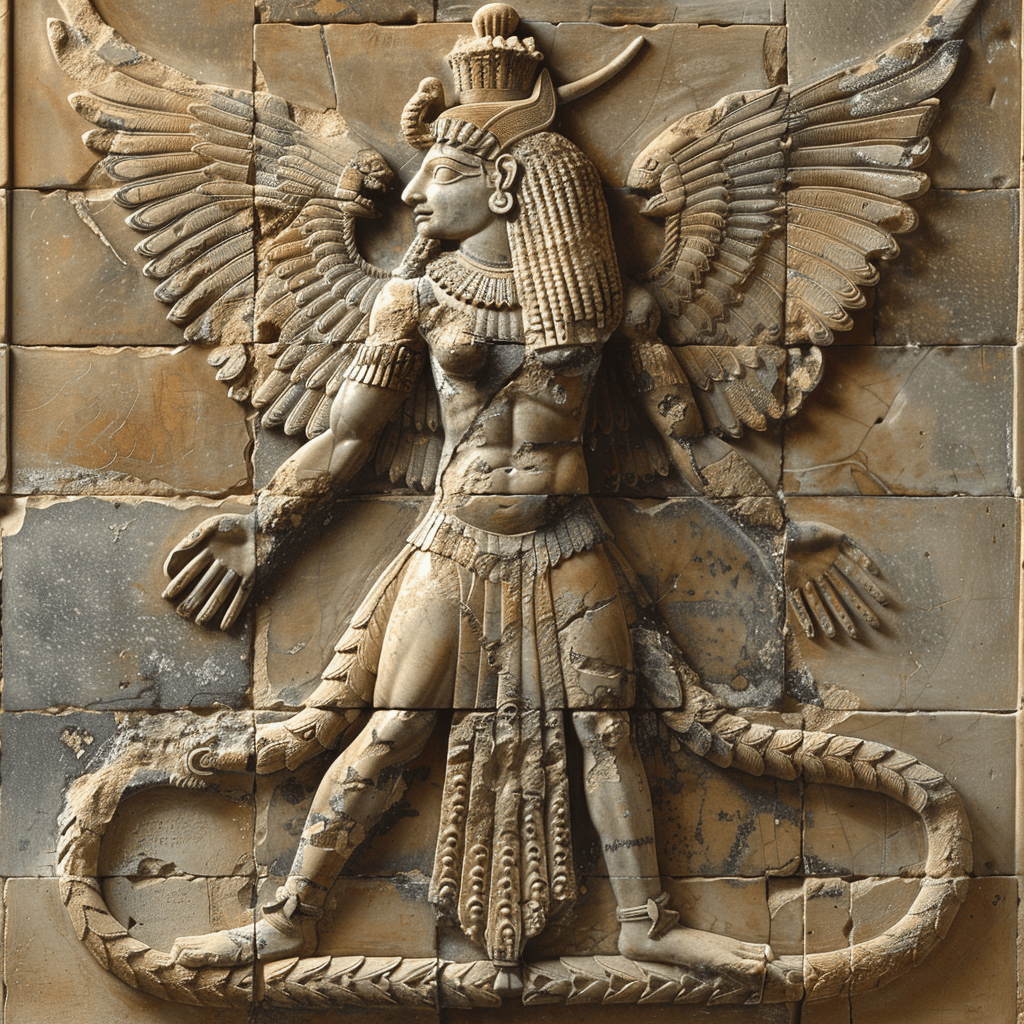
Tiamat

Ishtar (Inanna)

Enkidu

Nergal
Mesopotamian mythology Creatures

Apkallu

Ugallu
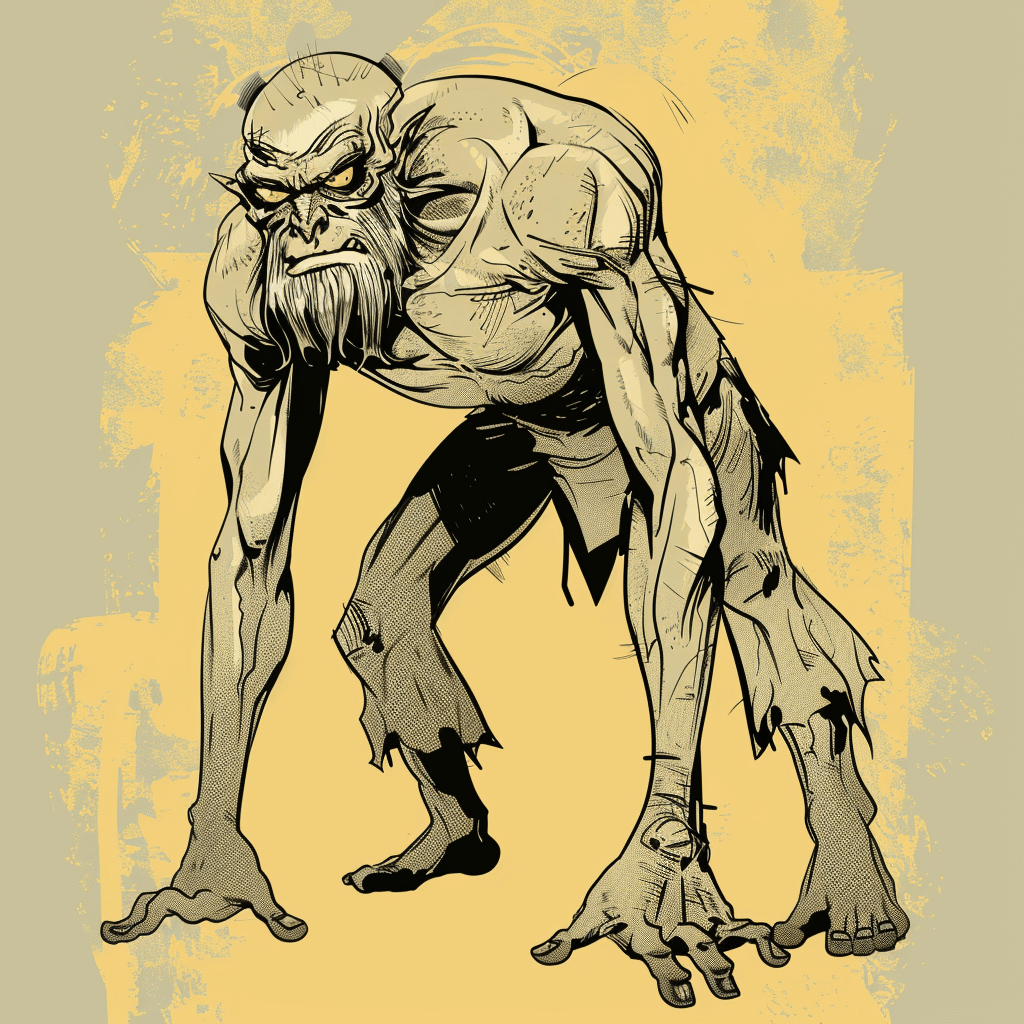
Humbaba

Utukku

Amhuluk
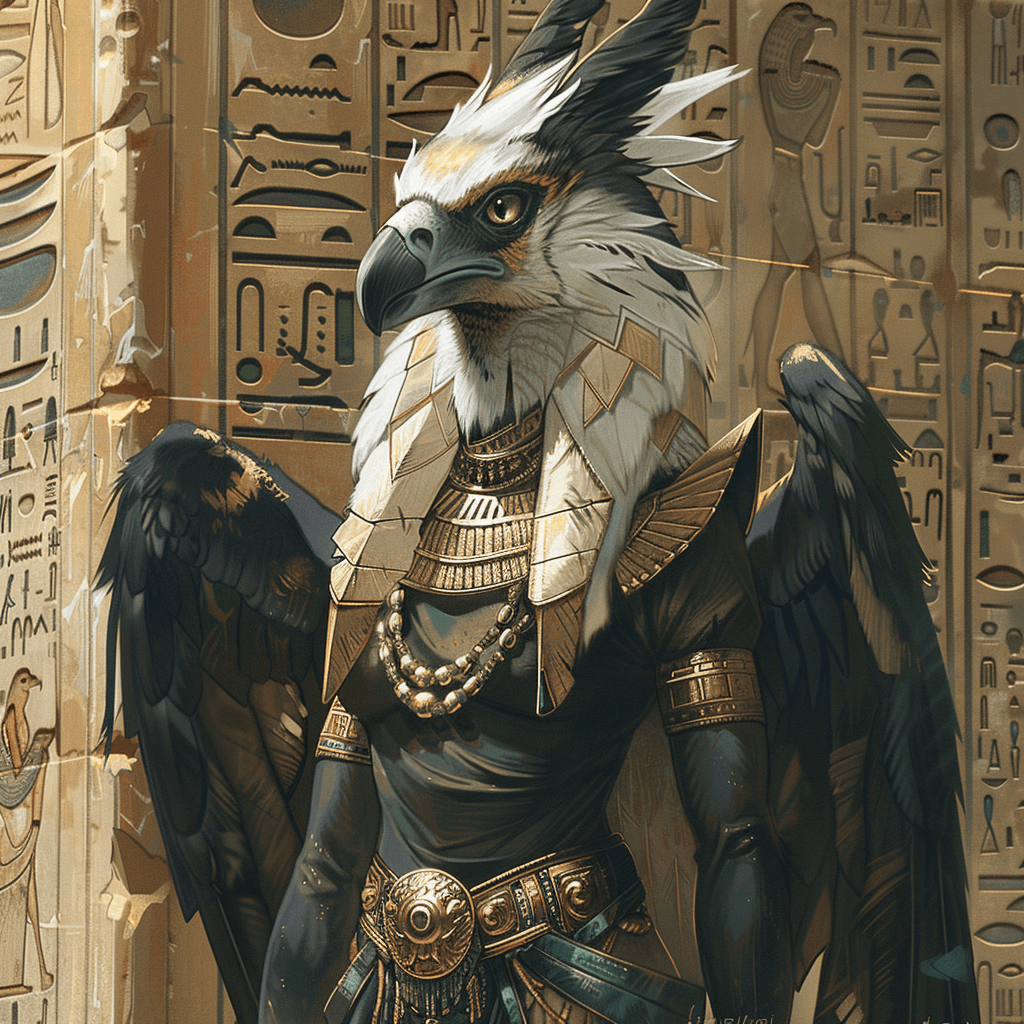
Lamashtu
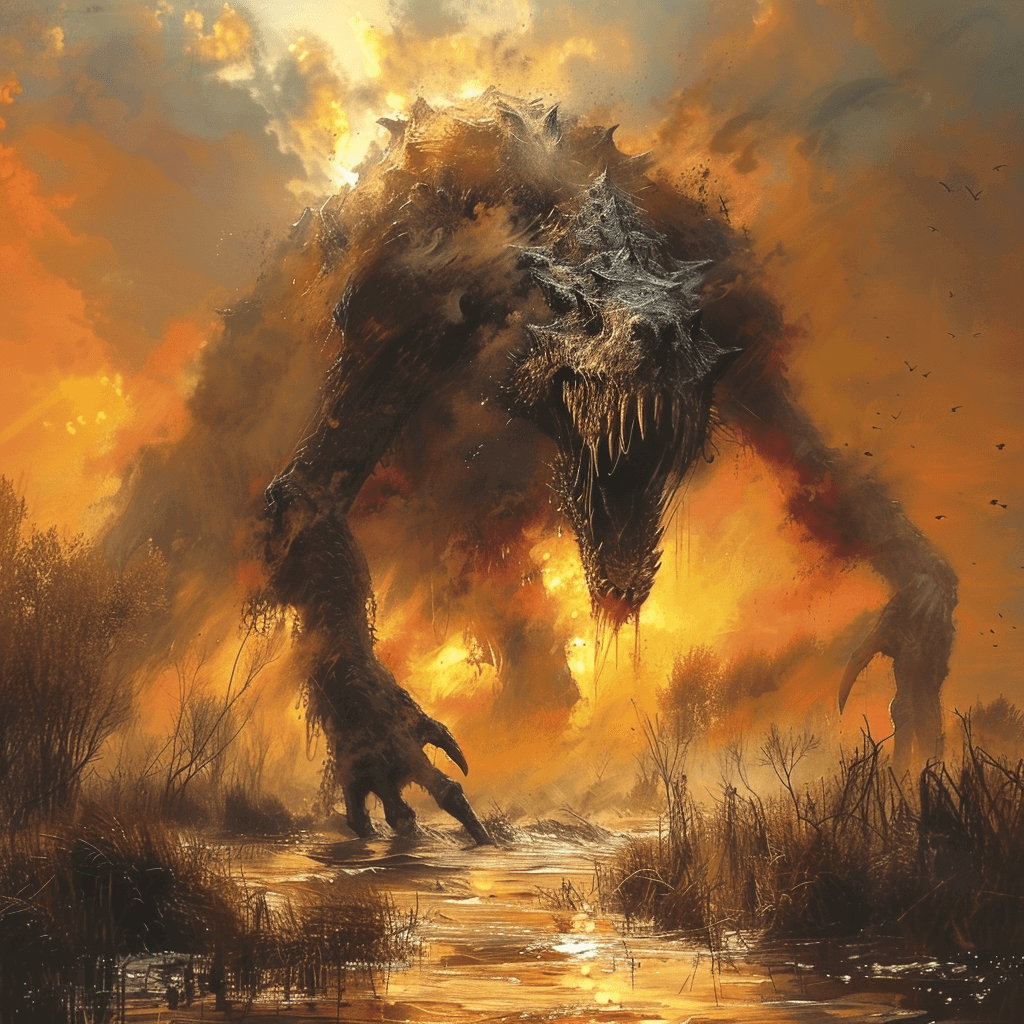
Sirrush
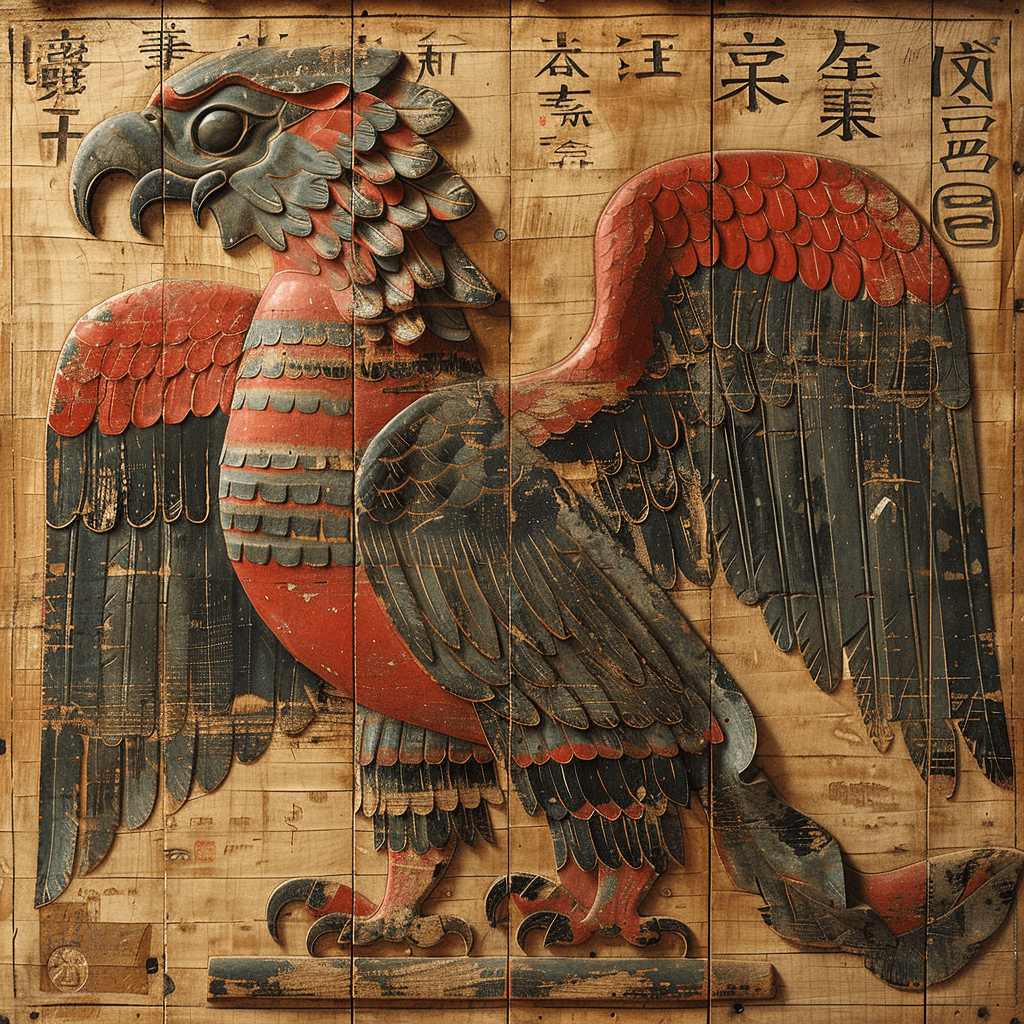
Anzu
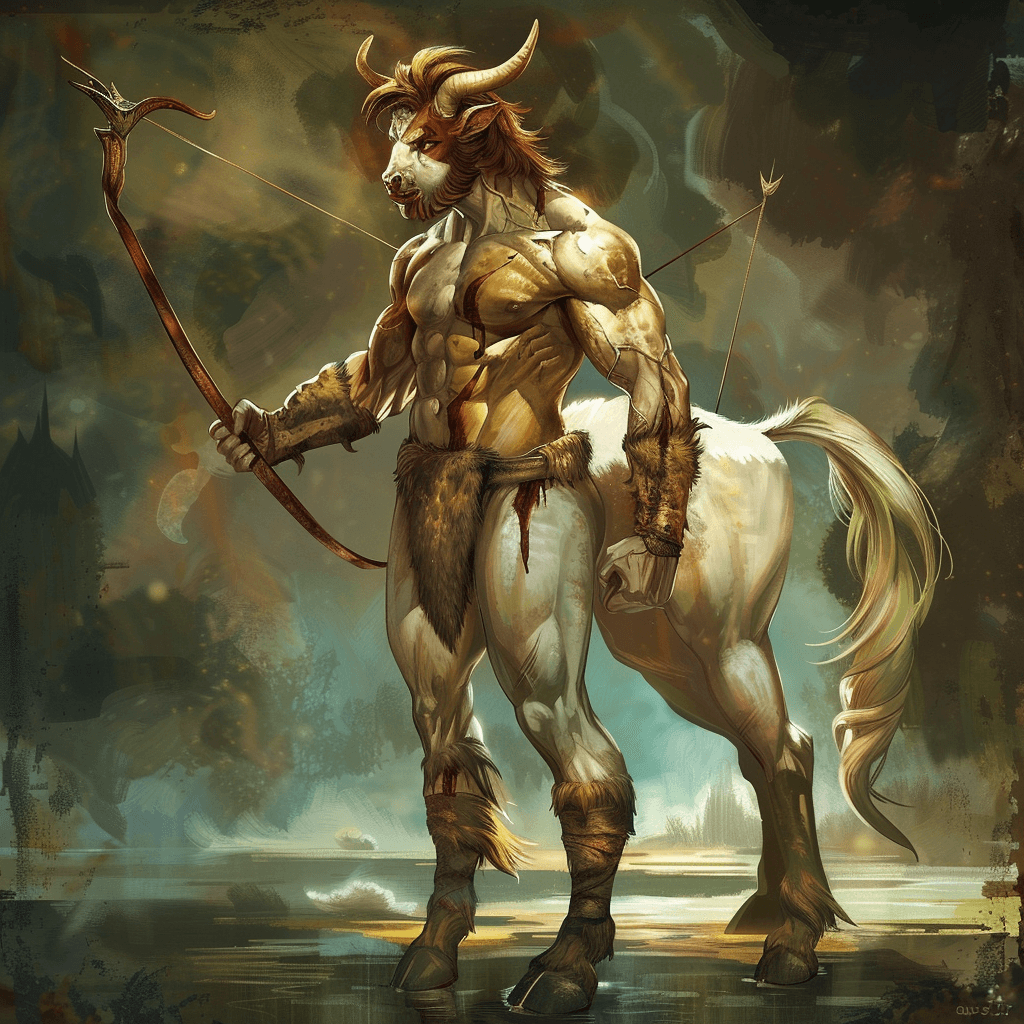
Urmahlullu
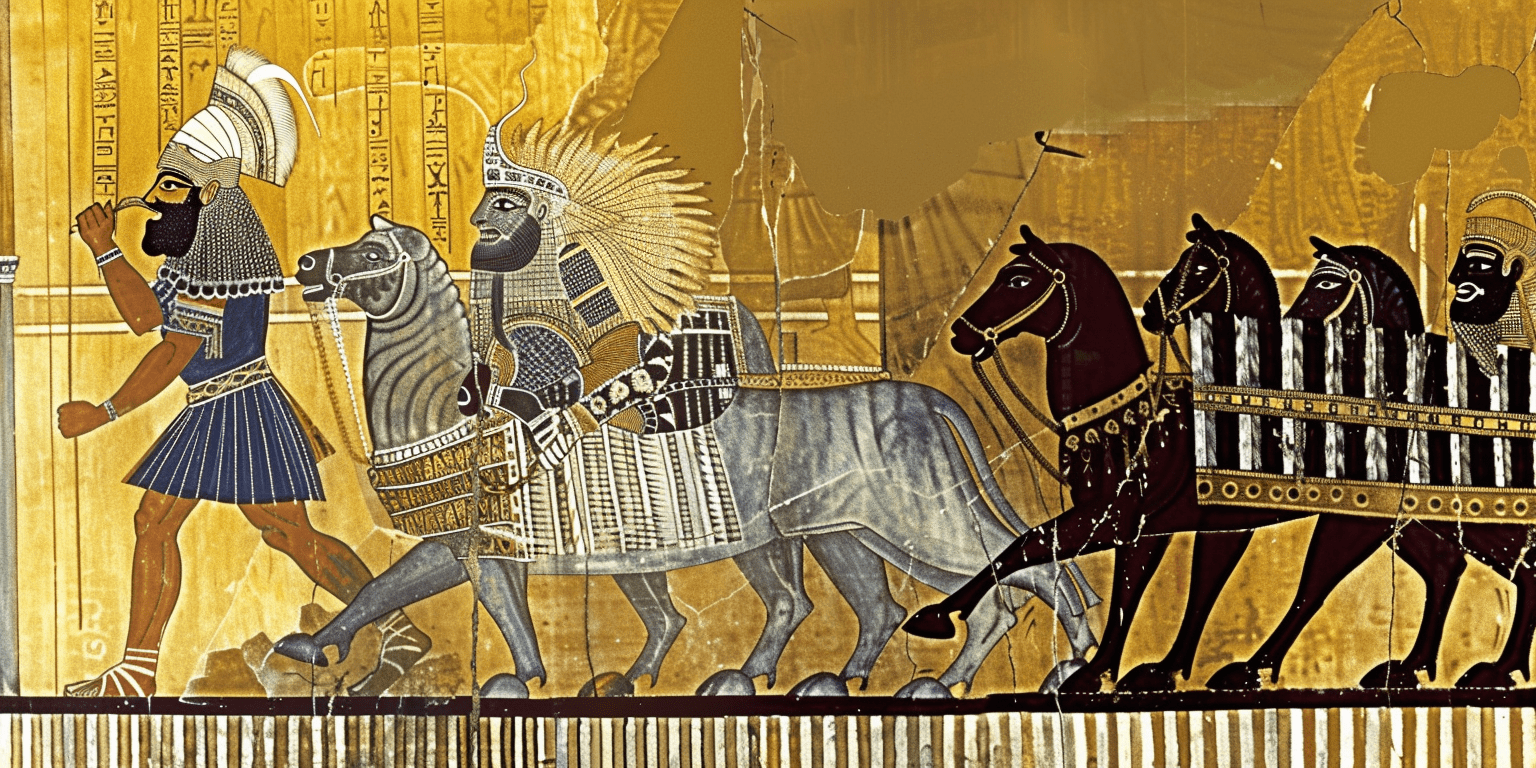
Shedu
Mesopotamian mythology Books

The Epic of Gilgamesh

Gods, Demons, and Symbols of Ancient Mesopotamia

The Babylonian Gilgamesh Epic









